|
|
|
This mini-website is dedicated to Actinomycin D and nothing but Actinomycin D
This miniwebsite has been prepared by MGur on two purposes:
The first is a homage to my friend Yossi Berend,
The second is - a HTML homework in Bioinformatics class, the Open
University Jerusalem.
There is no fancy design, nor sofisticated JS, but I think I may gain a
honorable web ranking. Shall we see that? Good. please test
my actinomycin web position
| [ | what is Actinomycin D |
| [ | the physical data of Actinomycin D |
| [ | the formula and 3D image if Actinomycin D |
| [ | what is Actinomycin D used for |
| [ | where to buy Actinomycin D |
| [ | References |
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Actinomycin D is an inhibitor of DNA-dependent RNA synthesis. It binds specifically to dG (3´-5´)dC site of DNA
Actinomycin-D is also
marketed under the following names: Dactinomycin, Cosmegen®, Actinomycin
IV, Actinomycin C1
Physical Properties of Actinomycin D
Appearance: Orange/red powder
Molecular formula: C62H86N12O16
Molecular weight: 1255.4
Melting point: decomposes at 241.5-243EC
E1%(244nm) = 281 (methanol)
E1%(441nm) = 206 (methanol)
EmM(240 nm) = 34.1 at 240 nm (methanol)
EmM(443 nm) = 24.4 (methanol)
Optical rotation: -315E(c = 0.25% in
methanol at 28EC)
he formula and 3D image if Actinomycin D
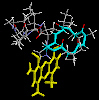 Click on the image to explore the
Click on the image to explore the
3D shape of the Actinomycin D molecule.
To take the full
advantage you should
download the
MDL plugin.
what is Actinomycin D used for :
Actinomycin D is one of the older chemotherapy drugs which has been used in therapy for many years. Actinomycin D is marketed as red, highly hygroscopic crystallic powder. Actinomycin D solution is a clear, yellow liquid which is administered intravenously and most commonly used in treatment of the following cancers: Gestational Throphoblastic cancers, Testis, Wilm's Tumor, Rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing's Sarcoma
The structure was determined by atomic structure and amino acid sequence.
"Dactinomycin is an antibiotic used for its antineoplastic properties in the
treatment of various malignant neoplasms including Wilm's tumour, and the
sarcomas. Adverse effects include bonemarrow depression and gastrointestinal
toxicity; it is extremely irritating and extravasation produces severe tissue
damage."5
The compound inhibits the proliferation of cells in a nonspecific way by
forming a stable complex with double-stranded DNA (via deoxyguanosine residues),
thus inhibiting DNA-primed RNA synthesis. It also causes single-strand breaks in
DNA.5,6,10 It is used in cell culture as a selection agent; suggested
working concentrations range from 0.01 to 2 mg/mL,
but typically 1 mg/mL.4
Actinomycin D binding to yeast in ribosomal RNA has been studied.11
The sensitivity of various strains of E. coli to actinomycin D and the mechanism
of binding has been studied.12,13
Actinomycin D is a highly toxic, carcinogenic, teratogenic and mutagenic
compound, and a possible sensitizer. Please consult the Material Safety Data
Sheet for appropriate handling.3
Products A1410 and A4262 differ slightly in purity. Sigma offers A9415
(cell culture tested) and a water-soluble formulation A5156. Each vial contains
1 mg actinomycin D and 49 mg mannitol.
1. Merck Index, 11th ed., p. 441, #2804 (1989).
2. Meienhofer, J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 92, 3771 (1970).
3. Sigma-Aldrich MSDS information.
4. Sigma data.
5. Martindale: The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed., Rynolds, J.E.F., ed.,
473 (1993).
6. Data for Biochemical Research, 3rd ed., Dawson, R.M.C. et al., eds.,
p. 256-257 (1986).
7. Rapp, R.P. et al., Drug Intelligence and Clinical Pharmacy, 18, 218
(1984).
8. United States Pharmacopeia, XXII, p. 379 (1990).
9. D'Arcy, P.F., Drug Intelligence and Clinical Pharmacy, 17, 532
(1983).
10. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 8th Ed., Goodmand and
Gilman, eds. (Pergamon Press, 1990), p. 1240-1241.
11. Waltschewa, L.W., FEBS Lett., 111(1), 179 (1980).
12. Singh, A.P, et al, Can J. Microbiol., 18(6), 909 (1972).
13. Cavalieri, L.F. and Nemchin, R.G., Biochim Biophys. Acta, 166(3),
722 (1968).
recent publications
Binding of Actinomycin D to Single-Stranded DNA of Sequence Motifs d(TGTCT(n)G) and d(TGT(n)GTCT)
The effect of space flight on the production of actinomycin D by Streptomyces plicatus.
where to buy Actinomycin D
| A.G. Scientific | L/K/T/ laboratories | ||||
|
[top]
 |
|